Technology has been indispensable in dealing with disasters with increased efficiency, expediting relief measures, and providing humanitarian support. Now, when the world is reeling under a massive outbreak of the coronavirus, Covid-19 contact tracing apps have emerged as a key recourse for governments.
These Bluetooth-enabled apps and platforms have the capability of tracking even small movements of people in a bid to secure lives from this dangerously contagious respiratory disease.
India among early movers
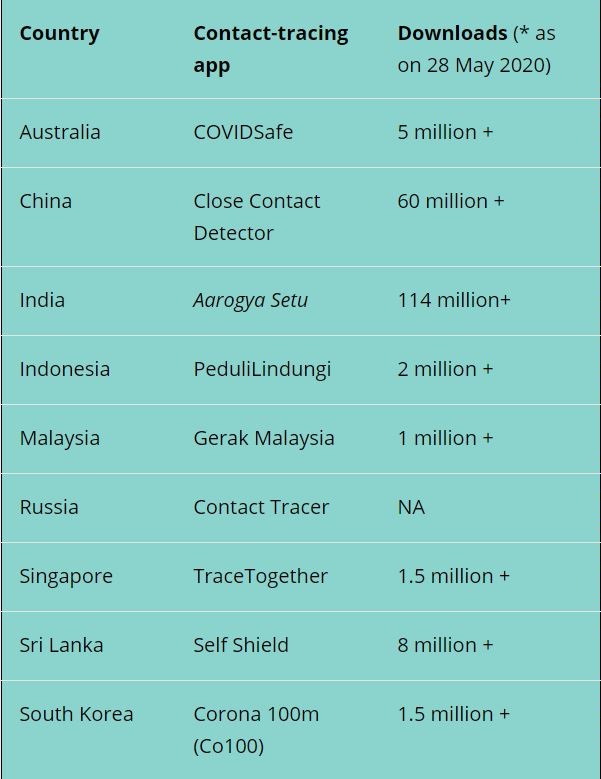
Australia, Singapore, Ghana, Israel, India, South Korea, and Saudi Arabia are among the countries that have already launched their respective coronavirus tracing apps. Many others are working to create similar tools. Apart from individual countries, global internet giants such as Apple and Google are also marshaling their resources to build tools to locate any potential virus carriers.
India launched its coronavirus contact tracing app Aarogya Setu on 2 April 2020. Better World spoke to Dr. Pavan Duggal, one of the top cyber law experts in the country and security and cyber law consultant Anuj Agrawal in this regard. They generally agree with the view that India has made a good start and taken some key steps in the right direction (click here to read full interview of Dr. Duggal).
Dr. Pavan Duggal: Good intentions, but it’s work in progress.
Anuj Agrawal: Data is only for Covid-19 control.
Dr. Duggal is of the opinion that it is a work in progress. “The overall intention of everyone is noble. It’s about defeating coronavirus. The earlier approach adopted by the government was neither prudent nor feasible (launching an app that was insecure and had concerns about privacy). Now, by taking these steps, the government has shown that they are taking criticisms seriously and are constructively trying to identify how to make it better. Making it open source is just a first step toward transparency. By announcing the Bug Bounty program, the government is also encouraging people to come forward and share the app vulnerabilities,” he observes.
Security and cyber law consultant Anuj Agrawal also feels that the new approach is definitely in the right direction. “Initially, many people were skeptical to use this app as they feared that this might put them under the government’s surveillance radar. But the government has made it clear that their intentions are truly wise, and they are concerned about user privacy as well. One also needs to remember that users are incidentally at risk of sharing their data with almost every downloaded application, and here the government has promised that they will only use this information to combat a severe disease,” he emphasizes.
More questions than answers?
The app development efforts globally, for tracing and containing the spread of the virus, are prima facie, laudable. However, critics allege, there is more to these apps than meets the eyes. The big worries are that these apps have started gathering the humongous amount of confidential data of billions of people worldwide, keeping track of their every movement and leaving their crucial information vulnerable to misuse.
Concerns around privacy and security are raising eyebrows and many industry experts have noted that these contact-tracing applications could end up putting sensitive personal information at risk. Some key questions in this regard are: Are these apps efficient to serve the intended purpose? How will the government process user data? What will be done with the data once the pandemic is over? Is there a surety that user data cannot be hacked and used for fraud and identity theft?
Privacy and security concerns
Amnesty International, a UK-based non-governmental human rights organization recently disclosed a critical lacuna in the configuration of Qatar’s Ehteraz contact-tracing app. It says that the bug could be exploited by cyber attackers to access highly sensitive personal information, including the names, national IDs, health status, and location data of more than a million users.
“Currently more than 45 countries have, or plan to, roll out Covid-19 contact tracing apps. Governments around the world, including Australia, France, Italy, the Netherlands, and the UK, are rushing to embrace digital tools which undermine privacy, have not yet been proved to be effective, and could put individuals’ security at risk,” it adds.
Besides, critics say it is not proven that these apps are helping authorities to restrict the outspread of Covid-19. Since the success of such apps is highly dependent on correct responses submitted by an individual user, one cannot be fully sure whether the information shared is veracious.
Moreover, these apps are not designed to work on the basis of sample denominators and require a large population to download and use it for accomplishing effective results.
For instance, Singapore’s TraceTogether, which was initially considered one of the best contact-tracing apps in the world, failed to highlight the revival of Covid-19 cases in many localized areas because only 20% of the country’s population was using it. Most of the smartphone users in Singapore cited data privacy as a major concern which was prohibiting them to use the application.
Clearly, a significant amount of effort is required to address the challenges related to ailing security architectures of such apps to encourage people at large to use them.
India setting an example?
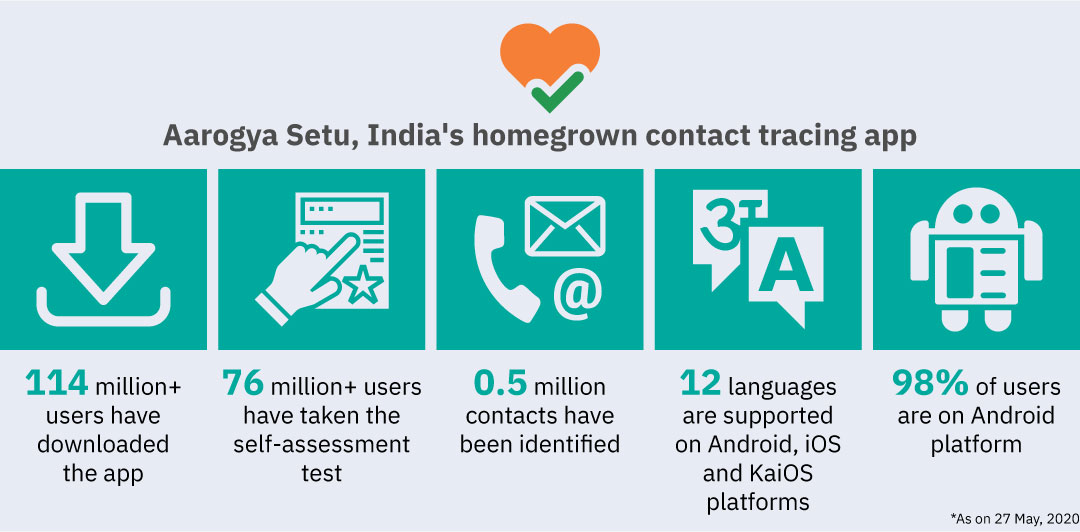
India launched the Aarogya Setu mobile app as part of its efforts to limit the spread of Covid-19. According to the Government of India, the app has already been downloaded by over 114 million users as on 26 May, surpassing any other contact tracing downloads in the world. India has also made the usage of this app compulsory for all its citizens while using public transport or going to offices.
The Aarogya Setu app too has invited criticism from many corners because of its mandatory information collection diktat by seeking continuous Bluetooth access and location data from users. Moreover, incomprehensible terms and conditions escalated fears that the government was trying to take advantage of the Covid-19 situation and use data for other purposes, which could compromise the freedom of individuals.
The Indian government has said that all data will remain anonymous and used only for the purpose of identifying positive Covid-19 cases. However, it could not give satisfactory answers related to the possibility of data theft and proceedings of collected information in the post-pandemic situation.
Facing criticism and backlash, the authorities went back to their boardrooms to address some of the issues. Recently, they have come up with a slew of improvements. Not only has the government rolled back the mandatory directive, but it has also opened the source code of the app’s Android version, thus enabling developers to inspect the source code and suggest modifications. Countries like the UK, Australia, Singapore and Israel also have open-source apps, making them transparent and verifiable.
In a first, the Government of India has also launched a ‘Bug Bounty’ program with the aim of identifying any security loopholes that may be exploited by potential hackers. (Read: Govt opens source code for Aarogya Setu, launches rewards program)
Dr. Duggal, however, adds that in spite of these positive steps, a lot still needs to be done to make this app truly secure. “This app still hides more than it speaks and when you read the terms and conditions, it clearly states that it is capturing data every 15 minutes and only sending the data to the server if the user is found Covid-19 positive. The question is: where does the sensitive personal information go if the user isn’t established as a Covid-19 patient?”
Steps ahead
There is no doubt that digital technologies offer whopping benefits and could play a strong role in identifying and controlling Covid-19 cases. However, none of these benefits could be translated into success if people start fearing these apps and see them as the government’s way of intruding into their private lives.
Throughout the world, we’ve witnessed numerous instances of cyberattacks on government databases. For example, recently, it was widely reported that hackers leaked on the dark web sensitive details of 18 lakh Indian citizens, including Aaadhar card numbers. Well-informed citizens cannot be allured to share crucial information on the pretext of a crisis. They need a strong assurance and concrete plan with respect to the privacy of their data.
Hence, countries need to find a way out to collect data anonymously and store it in a way that it does not get leaked to hackers or marketers.
Authorities also need to update their citizens whether and how these apps are helping them flatten the Covid-19 curve. Else, they will continue to be criticized as tools that could be exploited easily by hackers. To effectively utilize the benefits of technological innovations, governments need to safeguard the privacy of their citizens.









0 Comments