The Covid-19 pandemic has abruptly disrupted the growth projections for almost all sectors and industries, and the energy sector is no exception. Pandemic-induced lockdowns have triggered a precipitous decline in energy demand, with a boon also coming in the form of significantly reduced carbon emissions. Renewables are under threat of cheap oil.
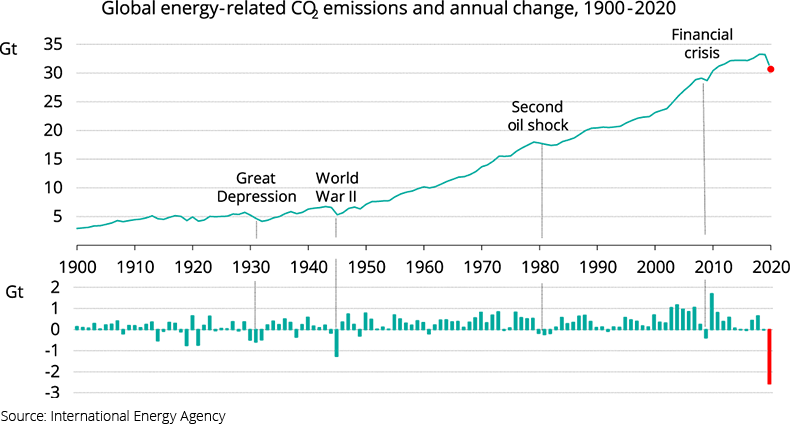
CO2 emissions have dropped the most ever due to the Covid-19 crisis, says a latest report from International Energy Agency (IEA). “Global energy-related CO2 emissions are set to fall nearly 8% in 2020 to their lowest level in a decade,” it says.
The report, however, warns, “Experience suggests that a large rebound is likely post crisis.”
In the recently published Global Energy Review, IEA, also says that due to the ongoing crisis, the energy demand is expected to fall by 6% in 2020, which is seven times the decline since the global financial crisis of 2008. This fall is equivalent of the energy demand from all of India, a nation of 1.3 billion people and the world’s third largest consumer of energy.
The partial to complete lockdown of global economies has triggered a massive slump in demand for fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas. Due to the suspension of the international as well as inter-state and even intra-state travels, oil demand is expected to see the biggest drop in demand, threating to erase gains accrued in nearly a decade.
Green-technology market observers see this decline as a staggering blow to the clean energy momentum gained in the recent years. However, it is also true that if we decide to take a proactive approach, this could be a monumental opportunity to elevate our focus on renewable energy endeavors.
Let us analyze how the current situation could impact our sustainable future.
IEA stays bullish on renewables
“Renewables are set to be the only energy source that will grow in 2020, with their share of global electricity generation projected to jump thanks to their priority access to grids and low operating costs. Despite supply chain disruptions that have paused or delayed deployment in several key regions this year, solar PV and wind are on track to help lift renewable electricity generation by 5% in 2020, aided by higher output from hydropower,” notes IEA in its report.
A report titled Mapping India’s Energy Subsidy 2020, conducted by the International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD) and the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW), try to examine how the Government of India (GoI) has used subsidies to support different types of energy. It states that the Indian government is still providing over seven times larger subsidies for fossil fuels as compared to subsidies for alternative energy. The recent world oil prices crash provides an opportunity to India, which can look at freeing up revenue by temporarily eliminating petroleum product subsidies while announcing stimulus for those companies who brace clean energy transition. For instance, due to the low oil prices, industry may witness a short-term dip in the electric vehicle uptake or deter the economic consumption of biofuels. To neutralize this, government should introduce electric vehicle incentives as part of the economic stimulus packages.
Industry observers see this as an ideal time to be investing in renewable energy. Not only it enables countries to create new jobs and make economies stronger, but it will also help us create a more resilient and better world. “It is still too early to determine the longer-term impacts, but the energy industry that emerges from this crisis will be significantly different from the one that came before,” notes Dr Fatih Birol, the IEA Executive Director in the Global Energy Review.
Dilemma for governments
It is apprehended that many countries could shift focus away from renewable energy efforts as their singular focus would be to restart up their economic engines as quickly as possible. They are quite likely to go for the traditional energy sources, owing to the sharp decline in their costs. In particular, oil prices are at a historical low, with the Brent crude having traded even at sub-dollar levels for a while in April 2020.
The triad of oil, gas, and coal form the core of the mainstream energy sector and any further disruption or closure of it could be crippling for the global economy itself. In India, for instance, almost 5% of the government’s total revenues from customs and excise, come from Reliance Industries Ltd., which in turn has most of its revenues coming from its oil refinery business.
Structural changes are needed
Considering the ongoing crisis, timely adoption of clean energy resources would be more significant than ever. United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP), in a recently published blog, notes that any suspension of clean energy efforts could pose grave threat to vulnerable communities of the world, especially in the Asia-Pacific region. It states that on the clean cooking front, slow progress in mainstreaming clean cooking solutions could see a dangerous combination of indoor air pollution and Covid-19. In this context, it notes, “Scientists are investigating links between air pollution and higher levels of coronavirus mortality, with preliminary results showing probable correlation between the two.”
Indeed, it is important for governments to plan and implement structural changes by earmarking requisite investments in transitioning to clean energies. Once the pandemic wanes, everyone would be busy taking decisions that could help kick-start economies. So to ensure that clean energy technologies feature substantially in the forthcoming recovery plans, there is a need to take some strategic decisions now. For a growing economy like India, which has been witnessing one of the highest growth rates in carbon dioxide emissions (CO2), it is extremely vital to prioritize clean energy transition.
What’s in it for India?
For India, while crude oil would continue to play a critical role at this stage of development in meeting country’s energy requirements, the Government had earlier set out a road map for reducing India’s crude oil imports by 10% by 2022. India’s Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas and Steel Dhamendra Pradhan, had said in a keynote in January 2020, “We are in the process of developing new strategies and initiatives to achieve this target. We are working towards transformation to a gas-based economy, tapping into indigenously produced biofuels, apart from adopting renewable energy and energy efficiency measures, to achieve the much-needed carbon reductions. As part of the energy transition, decarbonization of the energy sector is picking up momentum in India.”
One also needs to be cognizant of the long-term repercussions, if we do not step up and accelerate the development of renewable energy sources such as wind, solar PV, and hydropower.
India has the opportunity to leverage low costs of crude oil to shift subsidies from fossil fuels to renewable energy brackets. This could, in fact, help accelerate the transition to clean energy rather than deaccelerating it.
If India could succeed in mainstreaming the renewable energy sector, it would also be able to insulate it from oil price fluctuations in future. This would increase the country’s attractiveness from an investment perspective too, and consequently make its economy more sustainable in the long run.
Policymakers need not put economic recovery and sustainable energy goals in two different baskets. In the post-Covid-19 environment, polices around clean energy subsidies could very much be accelerated. This would help us build a better, cleaner world, where economic growth and sustainability coexist.















0 Comments