India has marked the beginning of super year of Biodiversity with the hosting of the 13th Conference of Parties (COP) of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS), an environmental treaty under the aegis of United Nations Environment Programme, from 17 to 22 February 2020 at Gandhinagar in Gujarat.
Union Environment Minister Prakash Javadekar has said that the year 2020 is a super year of Environment and will set the tone and tenor for the decade ahead. Highlighting the urgent nature of global environment issues including marine plastic litter, plastic pollution and microplastics, the Union minister said the issues cannot be solved by any one country alone.
 On the side-lines of the COP, the Union Minister met a delegation led by Norwegian Minister of Climate and Environment, Sveinung Rotevan. India and Norway have agreed to jointly tackle concerns related to oceans, environment and climate matters.
On the side-lines of the COP, the Union Minister met a delegation led by Norwegian Minister of Climate and Environment, Sveinung Rotevan. India and Norway have agreed to jointly tackle concerns related to oceans, environment and climate matters.
The Opening Ceremony and Plenary session of the COP takes place on 17 February followed by Side Events and Working Group meetings till the Closing Ceremony on 22 February. Prime Minister Narendra Modi will inaugurate the COP 13 via video conferencing. Numerous national and international organizations will showcase best practices in wildlife conservation during the course of the conference.
As the host, India shall be designated as the Presidency during the intersessional period following the meeting. The COP Presidency is tasked to provide political leadership and facilitate positive outcomes that further advance the objectives of the Convention, including steering efforts towards implementing the Resolutions and Decisions adopted by the Conference of Parties.
Migratory species of wild animals move from one habitat to another during different times of the year, due to various factors such as food, sunlight, temperature, climate, etc. The movement between habitats, can sometimes exceed thousands of kilometers/miles for some migratory birds and mammals. A migratory route will typically have nesting sites, breeding sites, availability of preferred food and requires the availability of suitable habitat before and after each migration.
India is home to several migratory species of wildlife including snow leopard, Amur falcons, bar headed Geese, black necked cranes, marine turtles, dugongs, humpbacked whales, etc.
The text of the Joint statement is as follows:
Meeting at the beginning of the ‘2020 Super Year’ for the environment, the Ministers stressed that they will do their share to ensure that the 2020s will be a decade of rapid action on climate and environment.
The two sides expressed interest to continue and strengthen the mutually beneficial cooperation on environment and climate between the two countries, including on ocean affairs.
Actions that target climate change and air pollution at the same time pose a win-win situation. The two sides recognized that such actions should be stepped up, and agreed to work together to raise this agenda.
The Ministers recognized that the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol for phasing down use of Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) could prevent up to 0.40C of warming by end of the century, Further, noting that universal ratification of Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol shall allow realization of its full potential.
The Ministers noted the results of the projects supported by Norway on issues / aspects related with phase down of HFCs. It was agreed to continue such projects for facilitating a smooth transition towards energy efficient solutions and technologies while phasing down HFCs.
If managed properly, the ocean holds the key to meeting many of the Sustainable Development Goals. Integrated ocean management is central to achieving a sustainable blue economy. In 2019 Prime Minister Modi and Prime Minister Solberg welcomed the signing of the MoU on India-Norway Ocean Dialogue and the establishment of the Joint Task Force on Blue Economy for Sustainable Development. The two Ministers were pleased with the progress that has been made under this MoU, including the establishment of the Marine Pollution Initiative. They were particularly satisfied that Norway and India will sign a Letter of Intent on integrated ocean management including sustainable Blue Economy initiatives.
The Ministers also noted the importance of delivering concrete, scalable solutions for ocean health and wealth at the UN Ocean Conference in Lisbon on June 2020.
The Ministers further noted the importance of sustainable management of chemicals and waste and welcomed the cooperation between India and Norway on the implementation of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants and on the minimization of discharge of marine litter.
The Ministers emphasized a shared understanding of the global and urgent nature of marine plastic litter and microplastics and underlined that this issue cannot be solved by any one country alone. They are committed to supporting global action to address plastic pollution and exploring the feasibility of establishing a new global agreement on plastic pollution.
 The Ministers agreed to support and work together with other political leaders to prompt a global and effective response to curb the direct and indirect drivers of biodiversity loss. They agreed to work together to deliver an ambitious, strong, practical and effective global biodiversity framework at COP15 of CBD to be held in Kunming, China, in 2020.
The Ministers agreed to support and work together with other political leaders to prompt a global and effective response to curb the direct and indirect drivers of biodiversity loss. They agreed to work together to deliver an ambitious, strong, practical and effective global biodiversity framework at COP15 of CBD to be held in Kunming, China, in 2020.
The Ministers further discussed the conservation of migratory species of wild animals. The Ministers recognized the importance of integrating ecological connectivity into the post-2020 global biodiversity framework.
The Ministers stressed that international supply chains and finance must de-invest from deforestation and destruction of nature and invest in companies and projects that improve smallholder livelihoods while promoting sustainable production and consumption. They agreed to continue the discussion on forests and deforestation free supply chains.
The Ministers stressed that the fifth United Nations Environment Assembly of the United Nations Environment Programme offers a good opportunity to call for greater international action on several environmental issues, in particular strengthening action for nature to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals.
Minister Rotevatn thanked Minister Javadekar for the great hospitality extended to him and his delegation during the visit. He invited Minister Javadekar to visit Norway and the Arctic, to further strengthen the collaboration between India and Norway on climate and environment.
Updated (17 Feb 2020, 10:47 pm):
India assumes presidency of UN body on Migratory Species for 3 years
The Thirteenth Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Migratory Species kicked off in Gandhinagar today in the presence of senior government officials, environment advocates, activists, researchers and biodiversity leaders from as many as 130 countries.
Inaugurating the key UN Summit via video conferencing Prime Minister Narendra Modi said that the CMS COP13 is of particular significance to India, which is known for its rich biodiversity and is one of the seven megadiverse countries in the world.
“India has four biodiversity hotspots – Eastern Himalayas, Western Ghats, Indo Myanmar landscape and Andaman and Nicobar Islands and home to as many as 500 species of migratory birds from across the globe”, said the Prime Minister.
The Prime Minister stressed that his government is committed to championing sustainable lifestyle, conservation and a green development model. He further added that in India’s role as the COP President in the next three years, it will look at conserving the Central Asian Flyway. To achieve this, India has prepared a National Action Plan. He further added that India is keen to facilitate action plans of other countries in this regard and aims at taking conservation to a new paradigm with active cooperation from all.
As President, India shall also look at strengthening cooperation with ASEAN countries for Indo-Pacific activities and conservation of marine biodiversity. He also added that India has launched the Marine Turtle Policy and Marine Standing Policy to address pollution caused by micro-plastics in the marine ecosystem. Other areas that will be under focus include transboundary cooperation, establishment of eco-development committees etc.
The Conference kicks off ‘“Super Year for Environment”, which will include a UN Summit in September and culminate in the UN Biodiversity Conference at the end of 2020, when a new global biodiversity strategy for the next decade will be adopted – the Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework.
India today assumed COP Presidency for the next three years with a focus on Collaborative Approach to tackle Biodiversity Issues. Assuming the presidency the Union Minister Prakash Javadekar said that CMS is very important to India and is at an exciting moment of development and the COP in India will mark the start of focused attention to migratory species and their habitats.



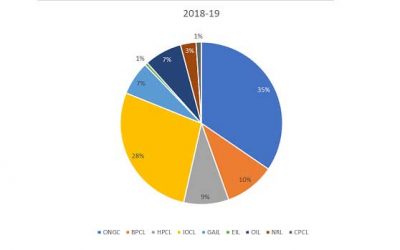







 In a major decision to give a boost to electric vehicles in country, the government has approved amendments in Electric Vehicle Charging Guidelines and Specifications. These Revised Guidelines and Specifications for charging infrastructure shall supersede the earlier guidelines and standards issued by the Ministry of Power on 14 Dec 2018.
In a major decision to give a boost to electric vehicles in country, the government has approved amendments in Electric Vehicle Charging Guidelines and Specifications. These Revised Guidelines and Specifications for charging infrastructure shall supersede the earlier guidelines and standards issued by the Ministry of Power on 14 Dec 2018.
0 Comments